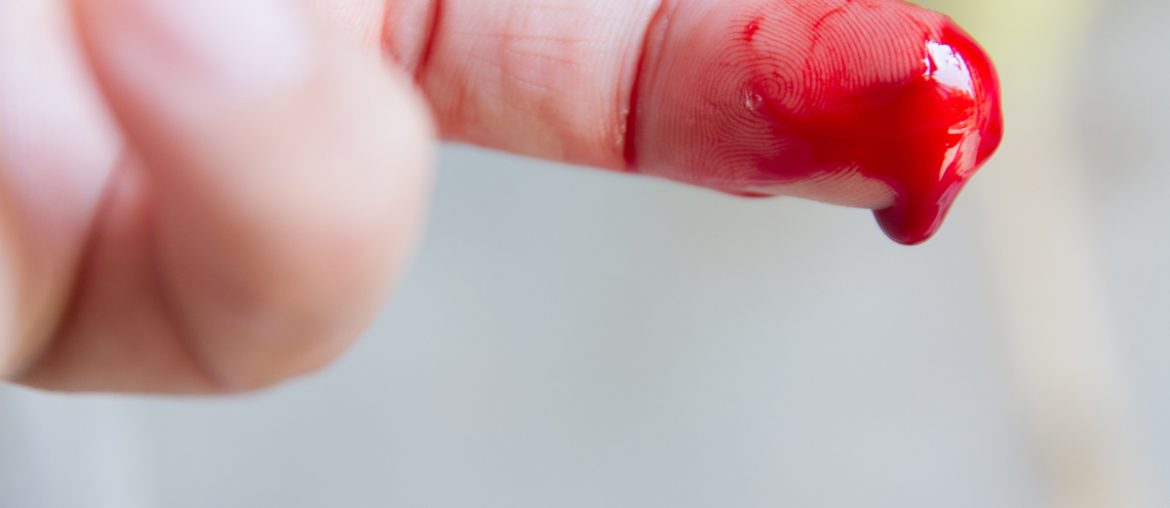
Hemophilia is an inborn genetic disorder where the blood doesn’t clot normally as the body does not have enough proteins called ‘clotting factors’. Due to this, bleeding produced by even minor injuries take a much longer time to stop. Hemophiliacs may bleed after a minor fall or may have bleeding inside the body without any real injury or triggering factor. There are an estimated 400,000 people suffering from hemophilia in the world today.
Hemophilia causes:
Hemophilia occurs due to a flaw in the gene that produces clotting factors. The extent of the flaw determines the quantity of clotting factors present. Hemophilia as a genetic defect is usually inherited, but cases of acquired haemophilia due to an autoimmunity have been on the rise as well. In acquired hemophilia, the clotting factors fail to work properly as the body produces antibodies to attack them.
Why are males more likely to suffer from Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is passed on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes (XX) and males have an X and a Y chromosome (XY). If a male has a hemophilia gene on his X- chromosome, there is no other normal X chromosome to counter it, unlike the females. This makes men sitting ducks to haemophilia. If a female has a faulty X chromosome, the other normal X chromosome will counter-balance it, protecting her from severe hemophilia. Thus, usually, women are carriers and may pass the gene at the time of conception to her male child.
Though the manifestations are same, there are two main forms of Hemophilia :
- Hemophilia A is lack of clotting factor VIII. One in 5000 male babies suffer from Hemophilia A. It is four times as common as Hemophilia B.
- Hemophilia type B is caused due to lack of factor IX. It attacks one in 30,000 babies.
Symptoms of Hemophilia:
- Easy bruises on the skin
- Bleeding into the joints or soft tissue leading to swelling and pain
- Abnormally excessive bleeding after injuries or after surgery
- Nose bleeds
- Bleeding in gums or tongue
- Uncontrolled bleeding after any dental work
- Presence of blood in urine
Symptoms of hemophilia in babies:
- Bleeding into the muscles after injection shots leading to a big bruise
- Infant’s heel bleeding after blood is drawn for tests
- Bleeding that goes on for a very long time (normally, a minor injury stops bleeding in under a minute)
- Bleeding under the scalp when the delivery is difficult or devices like forceps or vacuum are used.

Hemophilia treatment:
As of today, there is no cure for hemophilia. However, there is treatment available to replace the missing clotting factors. This replacement therapy can reduce the risks of bleeding episodes in the future.
One such treatment is gene therapy for Hemophilia. A hemophilac’s cells (usually liver cells, or muscle or fat cells ) are collected from the body. The cells are genetically altered and programmed to produce factor VIII or IX and are reinserted into the person. The person then can start producing their own clotting factors and essentially, gets cured of hemophilia.
Hemophilia researchers have found a novel way to block a particular protein that would offer more benefits than replacement therapy. Other researchers have also found a ‘turbocharged protein’ that has a very high clotting power to help reduce the costs of existing treatments for this clotting disease.
Living with hemophilia :
A diagnosis of hemophilia can leave many children and their parents deeply distressed. However, children born with hemophilia can lead a normal and fruitful life. They can even look forward to having children of their own in the future.
Watch this video to understand what is Haemophilia:





